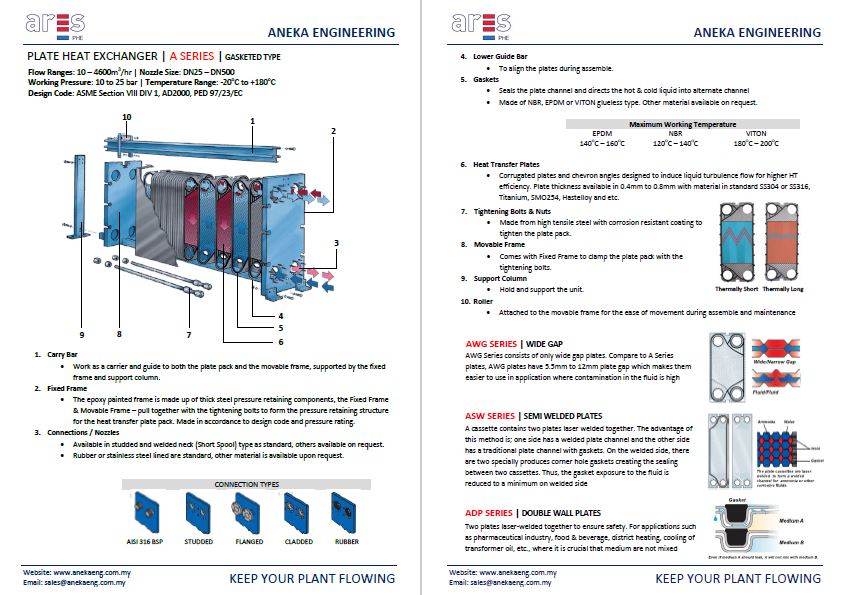
The working principle of plate heat exchanger is based on the heat transfer method between plates. Two fluid (hot and cold) enters the plate heat exchanger and by the help of gaskets, the fluids enters the correspondent plate and runs through diferent channels to achieve heat transfer without mixing with each other.
Structure of PHE Plate
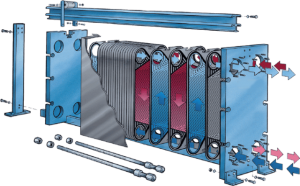
The main element of the plate heat exchanger is the metal plate which has herringbone pattern. The plates are pressed from various materials such as stainless steel to pure titanium with special design which creates turbulence to achieve highest heat transfer rates. The material of the plates depends on the medium passing through the plate heat exchanger. The plate thickness depends on the application and working pressure, which is usually between 0.4mm and 1mm.
PHE Gaskets Design
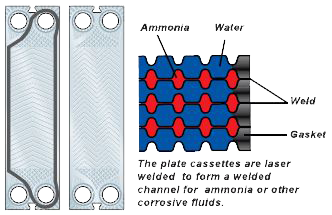

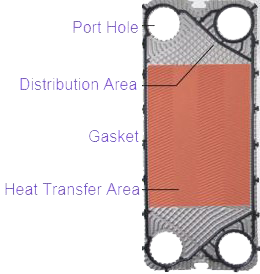
Each plate is equipped with a gasket which prevents the medium mixing with each other. Gasket material varies depending on the application, NBR and EPDM is the most commonly used throughout the world for plate heat exchangers. Some other material such as FKM, Silicone or other special material may be used.
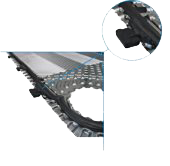
ARES Plate Heat Exchanger uses hang on gasket type where glue is not used at all. The glueless application makes it very easy for service and re-gasketting of our plate heat exchangers.
In addition to the heat transfer plate and gaskets, front and rear frame, bolts and nuts make up to the structure of the complete plate heat exchanger.
Type of Plate Heat Exchanger available:-
- Gasketed Type PHE
- Full Welded PHE
- Brazed PHE
- Modules Type PHE
- Nozzle size: 25mm to 500mm
- Flow rate: 15m3/hr to 4000m3/hr
- Industry used: Edible Oil Refinery, Power Plant, Pulp & Paper, Chemical Plant & Steel Mill.
- Application: Heating & cooling of edible oils, cooling of co-generation plant, cooling of wastewater.